Theme: Challenges and Advancements in Pharmaceuticals sciences
Global Pharma Summit 2020
Welcome to Global Pharma Summit and Expo 2020
We are very honour to welcome you all to attend the “Global Pharma Summit and Expo” which is happening on July 29-31, 2020 in Shanghai, China. The main theme of this conference is about Challenges and Advancements in Pharmaceutical Sciences which will give a worldwide Platform to all Scientific Professionals around the world. You can join our conference as an Oral Presenter, Poster Presenter, Delegate/Attendee or Exhibitor.
Global Pharma Summit covers various aspects of Bio-Pharmaceutics, Pharmaceutical Chemistry, Drug Targeting and Design, Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics in Drugs, Pharmaceutical Formulation, Bio-structural and Medicinal Chemistry, Pharmaceutical Nanotechnology, Novel Drug Delivery Systems, Smart Drug Delivery Systems, Toxicodynamics and Toxicology, Biomaterials in Drug Delivery, Vaccine Drug Delivery Systems, Medical Devices for Drug Delivery, Biologics & Biosimilars, Pharmaceutical Analysis, Pharmaceutical Process Validation, Pharmaceutical Packaging, Clinical Trials and Clinical Research, Pharmacognosy and Natural Products, Regulatory Affairs and Intellectual Property Rights, Industrial and Physical Pharmacy, Clinical and Hospital Pharmacy, Pharmacovigilance and Risk Management, Pharmacy Education and Practice.
Benefits of Attending:
- Attending Global Pharma Summit and Expo 2020 is an opportunity for you to expand your network with new people in the same field of Pharmaceutical Sciences.
- Exchange ideas and network with leading healthcare experts, Clinicians, researchers, pharmacovigiliants and other eminent Pharma professionals.
- Connect with senior-level executives from leading international pharmaceutical & biotechnology companies.
- Exposure to new and exciting companies ready for partnership and licensing opportunities in the U.S., Europe and Asia.
- Tremendous networking opportunities to meet numerous U.S., European, Japanese and Asian biotech and pharmaceutical companies in a single spot at once.
- Targeted partner selections through proprietary screening process and also a wide track of exhibitors to showcase the new and emerging technologies.
- Learn how to develop the right formulation and delivery strategy with a strong scientific and clinical mind-set inspired by innovative case studies.
- Platform for global investment community to connect with stakeholders in Pharma/Biotech sector and get certificates which recognizes your commitment towards your profession.
Who should attend?
- Directors, CEO’s of Organizations
- Business Development Managers
- Chief Scientific Officers
- R&D Researchers from Bio similar and Biologics Industries
- Professors, Associate Professors, Assistant Professors
- PhD Scholars
- Intellectual Property Attorneys
- Investment Analysts
- Association, Association presidents and professionals
- Drug development and discovery companies
- Formulation and Pharma Manufacturing companies
- Medical technology companies
- Students from Universities and institutes
- Intellectual property and legal organizations
- Investors and financial services providers
- Bio-clusters and incubators
- Government and public support agencies
- Cosmetic companies
- Generic drugs and Biosimilars
GLOBAL PHARMA SUMMIT AND EXPO Conference Highlights:
- 100+ Participation (70% Industry: 30% Academia)
- 7+ Keynote Speakers
- 20+ Plenary Speakers
- 1-2 Exhibitors
- 14 Innovative Educational Sessions
- B2B Meetings
Target Audience:
- Drug Delivery Technology Manufacturers
- Experts in Clinical Pharmacy and Pharmacology
- Academic researchers and Healthcare Institutions
- Research Heads and Scientific Professionals
- Distributors and Suppliers of Drug Delivery Technologies
- Pharmaceutical entrepreneurs
- Relevant Graduate and Postgraduate students
- Manufacturing Pharmaceutical products Companies
- Pharmaceutical Associations and Societies
Pharmaceutical Associations
Academy of Managed Care Pharmacy| American Association of Pharmaceutical Scientists| American Association of Colleges of Pharmacy| American College of Chest Physicians| American College of Clinical Pharmacy| American Heart Association| American Pharmacists Association| American Society of Consultant Pharmacists| American Society of Health-System Pharmacists| Board of Pharmacy Specialties| College of Psychiatric and Neurologic Pharmacists| Haematology/Oncology Pharmacy Association| Joint Commission on the Accreditation of Healthcare Organizations| National Association of Chain Drug Stores| National Community Pharmacists Association| Society of Critical Care Medicine| Society of Infectious Diseases Pharmacists| Chinese Pharmaceutical Association.
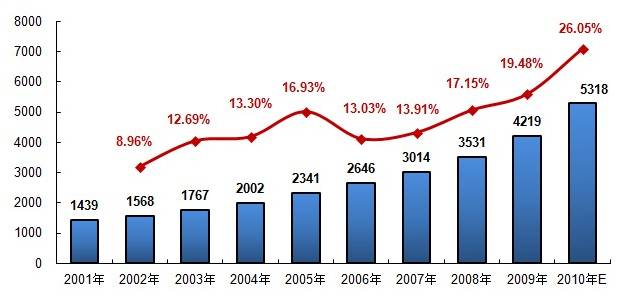
According to IMS Health Consulting, an international research company, in 2012 the size of the global pharmaceutical market reached $940 billion. In monetary terms it grew by 6%. In the future the sector is expected to grow at no less than 3% to 4% a year and if this happens the global pharmaceutical market is expected to reach $1.1 trillion by 2015 and will reach $1.2 trillion in 2016 and up to $1.5 trillion by 2020. The global demographic, epidemiological and economic changes are transforming the pharmaceutical market.
The pharmaceutical industry is directly impacted by the research conducted with prescription drugs, vaccines, and OTC drugs being manufactured based on findings from the study of life sciences. The world population is growing rapidly and is projected to raise from 7 billion in 2011 to 7.7 billion in 2020 and 9.6 billion in 2050, hence an increase in the demand for pharmaceuticals. The ageing process also affects the demand. By 2020 about 9.4% of the world population (719.4 million people) will be 65 or above, compared with 7.3% (477.4 million) in 2005 (UN, 2013). Clinical advances reinforce this trend. The improvements of the past few decades have already converted some previously terminal illnesses into chronic conditions, thus increasing long-term demand for pharma-co-therapeutics to manage these diseases. Spending on medicines will reach nearly $1,100Bn in 2015, reflecting a slowing growth rate of 3-6% over the five year period compared to 6.2% annual growth over the past five years. Absolute global spending growth is expected to be $210-240Bn, compared to $251Bn since m2005.
- Pharmaceutical Formulation
Pharmaceutical Formulation studies involve developing a preparation of the drug which is both stable and acceptable to the patient. For orally administered drugs, this usually involves incorporating the drug into a tablet or a capsule. It is important to make the distinction that a tablet contains a variety of other potentially inert substances apart from the drug itself, and studies have to be carried out to ensure that the encapsulated drug is compatible with these other substances in a way that does not cause harm, whether direct or indirect. In dealing with protein pre-formulation, the important aspect is to understand the solution behaviour of a given protein under a variety of stress conditions such as freeze/thaw, temperature, shear stress among others to identify mechanisms of degradation and therefore its mitigation.
- Biopharmaceutics and Pharmacokinetics
Biopharmaceutical Science includes study of the drug discovery and their development, along with their properties, both physical and chemical. Bio-Pharmaceutical Sciences session includes talks on diversified fields like Biopharmaceutics and drug disposition, Innovations in clinical development, Pharmaceutical technology, Drug discovery and design, Pharmaceutics and drug delivery, Routes of administration, Fundamental drug development and etc.
Pharmacodynamics, described as what a drug does to the body, involves receptor binding, post receptor effects, and chemical interactions. Drug pharmacokinetics determines the onset, duration, and intensity of a drug’s effect. Formulas relating these processes summarize the pharmacokinetic behaviour of most drugs.
- Pharmaceutical Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology is manipulation of matter on an atomic, molecular, and supramolecular scale. The earliest, widespread description of nanotechnology referred to the particular technological goal of precisely manipulating atoms and molecules for fabrication of macroscale products, also now referred to as molecular nanotechnology. A more generalized description of nanotechnology was subsequently established by the National Nanotechnology Initiative, which defines nanotechnology as the manipulation of matter with at least one dimension sized from 1 to 100 nanometres. It is therefore common to see the plural form "nanotechnologies" as well as "nanoscale technologies" to refer to the broad range of research and applications whose common trait is size.
- Drug Discovery and Development System
Researchers discover new drugs through insights into a disease process that allow researchers to design a product to stop or reverse the effects of the disease. Once researchers identify a promising compound for development, they conduct experiments to gather information on how it is absorbed, distributed, metabolized, and excreted, best dosage, Side effects, how it interacts with other drugs and treatments and its effectiveness as compared with similar drugs.
Drug expansion is the procedure of creating a new pharmaceutical drug to the global market once a lead compound has been found through the procedure of drug discovery. It includes pre-clinical research on microorganisms and animals, filing for regulatory statuses, such as via the United States Food and Drug Administration for an investigational new drug to initiate clinical trials on humans, and may include the step of obtaining regulatory approval with a new drug application to market the drug.
- Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics
Pharmacokinetics of a drug depends on patient-related factors as well as on the drug’s chemical properties. Some patient-related factors (e.g., renal function, genetic makeup, sex, age) can be used to predict the pharmacokinetic parameters in populations. Knowledge of pharmacokinetic principles helps prescribers adjust dosage more accurately and rapidly. Application of pharmacokinetic principles to individualize pharmacotherapy is termed therapeutic drug monitoring.
Pharmacodynamics, described as what a drug does to the body, involves receptor binding, post receptor effects, and chemical interactions. Drug pharmacokinetics determines the onset, duration, and intensity of a drug’s effect. Formulas relating these processes summarize the pharmacokinetic behaviour of most drugs.
- Pharmacology
Pharmacology focuses on the therapeutic effects of pharmaceutical substances and how they can be used most effectively for medical purpose. Toxicology and Pharmacology are both studies that involve in assessing the properties of chemicals and their actions on the body, but differ significantly in other areas. Toxicology is closely related to the adverse effects that can occur in living organisms that come into contact with chemical compounds. Toxicologists are also concerned with determining the risk of certain substances with risk assessment tools.
- Novel Drug Delivery System
Drug delivery systems control the pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, non-specific toxicity, immunogenicity and efficacy of drugs. NDDS is a combination of advance technique and new dosage forms which are far better than conventional dosage forms. Novel drug delivery system classified in to different types based on the diffusion types. Drug Delivery Carriers show great promise as drug delivery systems. Drug delivery may be either active or passive process. NTTD Increases the efficacy of the drug and decrease side effects. The global market for drug delivery systems is expected to rise at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5% and reach nearly $175.6 billion by 2021.
- Toxicology
Toxicology is the scientific study of harmful effects of chemical, biological and physical agents in biological systems that establish the extent of damage in living organisms. It includes observing symptoms, mechanisms, detection and treatments of toxic substances, in certain relation to the poisoning of humans. It consists of environmental agents and chemical compounds, as well as Pharmaceutical Compounds that are manufactured for medical use by humans. These substances may produce toxic effects in living organisms including disturbance in growth patterns, discomfort, disease and death. Factors that influence toxicity include the dose, the route of exposure, shape and structure of the chemical, the species, individual human factors and environment.
- Pharmacovigilance and Drug Safety
Pharmacovigilance and Risk Management comprises set of pharmacovigilance activities and interventions designed to identify, characterise, prevent or minimise risks relating to medicinal and therapeutic products including the assessment of the effectiveness of their clinical interventions and combination therapies. Drug industry need to promote companies in pharmacovigilance practice to use information technology and to review software’s used in pharmacovigilance and clinical trials. Monitoring unlicensed, off labels and orphan drugs is major task in risk management.
Researchers discover new drugs through insights into a disease process that allow researchers to design a product to stop or reverse the effects of the disease. Once researchers identify a promising compound for development, they conduct experiments to gather information on how it is absorbed, distributed, metabolized, and excreted, best dosage, Side effects, how it interacts with other drugs and treatments and its effectiveness as compared with similar drugs.
- Nano Particles
One of the big challenges of medicine today is to deliver drugs specifically to defected cells. Nano particulate drug carriers have the potential to answer to this call, as nanoparticles can cross physiological barriers and access different tissues, and also be provided in a targetable form aimed at enhancing cell specificity of the carrier. Recent developments within material science and strong collaborative efforts crossing disciplinary borders have highlighted the potential of mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSNs) for such targeted drug delivery. Relatively straightforward inside-out tuning of the vehicles, high flexibility, and potential for sophisticated release mechanisms make these nanostructures promising candidates for targeted drug delivery such as ‘smart’ cancer therapies.
- Biologic and Biosimilar Drugs
Structural biology is a branch of molecular biology, biochemistry, and biophysics concerned with the molecular structure of biological macromolecules (especially proteins, made up of amino acids, RNA or DNA, made up of nucleotides, membranes, made up of lipids) how they acquire the structures they have, and how alterations in their structures affect their function. This architecture, the "tertiary structure" of molecules, depends in a complicated way on each molecule's basic composition, or "primary structure." Biomolecules are too small to see in detail even with the most advanced light microscopes.
- Medicinal and Pharmaceutical Chemistry
Medicinal chemistry and pharmaceutical chemistry are disciplines at the intersection of chemistry, especially synthetic organic chemistry, and pharmacology and various other biological specialties, where they are involved with design, chemical synthesis and development for market of pharmaceutical agents, or bio-active molecules. Compounds used as medicines are most often organic compounds, which are often divided into the broad classes of small organic molecules and "biologics", the latter of which are most often medicinal preparations of proteins.
In particular, medicinal chemistry in its most common practice—focusing on small organic molecules—encompasses synthetic organic chemistry and aspects of natural products and computational chemistry in close combination with chemical biology, enzymology and structural biology, together aiming at the discovery and development of new therapeutic agents. Practically speaking, it involves chemical aspects of identification, and then systematic, thorough synthetic alteration of new chemical entities to make them suitable for therapeutic use.
- Drug Regulatory Affairs
Drug Regulatory Affairs refers to all aspects within the pharmaceutical development process and how they are subject to various degrees of regulation. The pharmaceutical law frame, guidelines covering Quality, Safety and Efficacy as well as Health Authorities' attitudes and requirements etc. It is a profession developed from the desire of governments to protect public health by controlling the safety and efficacy of products in areas including pharmaceuticals, veterinary medicines, medical devices, pesticides, agrochemicals, cosmetics and complementary medicines, and by the companies responsible for the discovery, testing, manufacture and marketing of these products wanting to ensure that they supply products that are safe and make a worthwhile contribution to public health and welfare.
- Drug Elimination and Clearence
Drugs are removed from the body by various elimination processes. Drug elimination refers to the irreversible removal of drug from the body by all routes of elimination. The declining plasma drug concentration observed after systemic drug absorption shows that the drug is being eliminated from the body but does not indicate which elimination processes is involved. Drug elimination is usually divided into two major components: excretion and biotransformation. Drug excretion is the removal of the intact drug. Non-volatile drugs are excreted mainly by renal excretion, a process in which the drug passes through the kidney to the bladder and ultimately into the urine.
- Pharma-co-economics
Health economics is a tool to help us prioritise different and sometimes competing health care interventions for these fixed resources and, in doing so, health care is treated as a commodity like any other. Knowledge of health economics coupled with political insight is essential to understand resource allocation and expenditure in a modern health care system. Pharmacists, with their unique knowledge of medicine, are crucial in using pharma-co-economics analysis to influence expenditure and distribution of resources on medicines. Design and management of pharma-co-economic studies
· Cost and burden of illness studies
· Drug utilization
· Budget impact analysis
· Modelling and simulations
- Vaccine Delivery System
A vaccine is a biological preparation that provides active adaptive immunity to a particular disease. Vaccine generally contains a component that is usually a disease-creating microorganism and is often made from weakened or killed forms of the microbe, pathogen, its toxins, or one of its surface proteins. There are many types of vaccine like – 1.Inactivated, 2.Attenuated, 3.Toxoid, 4.Subunit, 5.Conjugate, 6.Experimental, 7.Valance, 8.Heterotypic.
Immunization system contains two types of doses That is – Prime dose & Booster dose. Immunization failed if the patient ignores the booster dose. Booster doses are required to induce an effective immunity. For that reason to skip the booster dose, invention of new generation prophylactic and therapeutic vaccine are required to initiate more effective immunization.
- Quality Control and Quality Assurance
Quality control (QC) is a procedure or set of procedures intended to ensure that a manufactured product or performed service adheres to a defined set of quality criteria that meets the requirements of the client or customer. A major aspect of quality control is the establishment of well-defined controls. The role of Quality Impact Assessment & effectiveness checks is an essential operation of the pharmaceutical industry.
Quality Assurance (QA) is defined as a procedure or set of procedures intended to ensure that a product or service under development meets specified requirements. Quality assurance conferences aims at the need for Effective Internal and External Quality Assurance Auditing and it is required, by all active pharmaceutical ingredient (API)/bulk pharmaceutical chemical, medical device and finished pharmaceutical cGMP regulations published worldwide.
- Analytical Strategies for Pharmaceutical Products
Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry are extensively used in the formulation development stage of generic drug products. For certain selected analyses, Liquid Chromatography- Ultraviolet Detection (LC-UVD) and Gas Chromatography-Flame Ionization Detection (GC-FID) techniques may be deemed suitable. However, Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS) and Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS) are usually the techniques of choice when higher specificity and sensitivity are required. Occasionally, some spectroscopic techniques like Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR), light scattering, and Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS) are used in analysing PGIs/GIs.
- Pharmacognosy and Herbal Drug Action
Pharmacognosy the branch of knowledge concerned with medicinal drugs obtained from plants or other natural sources. Drug Action examines how the drug itself works in a living system, which is the definition of pharmacology. The action of the drug can be studied at the molecular level, in a cell, an organ, and in animals. Specialty fields within Drug Action include molecular biology, pharmacology, pharmacodynamics, toxicology, and biochemistry.
Pharmacognosy gives a sound knowledge of the vegetable drugs under botany and animal drugs under zoology. It also includes plant taxonomy, plant breeding, plant pathology, and plant genetics and by this knowledge one can improve the cultivation methods for both medicinal and aromatic plants.
- Paediatric Pharmacy
Paediatric drug specialists guide children and their parents about solution and write prescriptions as needed. They track their patients' therapeutic progress and ensure that there are no harmful drug interactions or unexpected side effects. Paediatric drug specialists regularly work in restorative offices like specialist's workplaces, drug stores, and healing facilities. Paediatric Pharmacy ensures safe and effective drug use and optimal medication therapy outcomes in children up to 18 years of age. Currently there are more than 1,100 BPS Board Certified Paediatric Pharmacy Specialists. Paediatric pharmacists counsel children and their parents about medication and write prescriptions as needed.
Conference Highlights
- Pharmaceutical Formulation
- Bio pharmaceutics and Pharmacokinetics
- Pharmacology
- Drug Discovery and Development System
- Novel Drug Delivery System
- Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics
- Toxicology
- Pharmacovigilance and Drug Safety
- Nano Particles
- Biologic and Biosimilar Drugs
- Medicinal and Pharmaceutical Chemistry
- Drug Regulatory Affairs
- Drug Elimination and Clearence
- Vaccine Delivery System
- Quality Control and Quality Assurance (QC & QA)
- Analytical Strategies for Pharmaceutical Products
- Pharma-co-economics
- Pharmacognosy and Herbal Drug Action
- Pharmaceutical Nanotechnology
- Paediatric Pharmacy
To share your views and research, please click here to register for the Conference.
To Collaborate Scientific Professionals around the World
| Conference Date | July 29-31, 2020 | ||
| Sponsors & Exhibitors |
|
||
| Speaker Opportunity Closed | |||
| Poster Opportunity Closed | Click Here to View | ||
Useful Links
Special Issues
All accepted abstracts will be published in respective Our International Journals.
Abstracts will be provided with Digital Object Identifier by
